What is the purpose of using a 3D CAD software?
In the various design offices, design is increasingly carried out with 3D CAD software. But what is the point of using 3D CAD software versus 2D?
Historically, the drawing board gave way to 2D drawing software and then to 3D CAD software.
2D software is a continuity of the drawing board in the digital era, but retains its limitations.
However, 3D software provides real added value in many areas, both from a technical and commercial viewpoint.
“Technically”:
- Save time through rapid modification and reuse of components and assemblies
- To manage increasingly complex structures
- Detecting design problems through collision management or simulation
- Make automatic calculations such as masses, areas, …
- Automatically output part detail plans (cuts, projections, sections)
- List the parts to be manufactured, the cuttings, the bills of material
- Move directly to manufacturing with an interface for CNC machines or 3D printing
- Facilitate their production and reduce the risk of error
“Commercially”:
- Communicate with the 3D model internally or with its customers or subcontractors
- Boost the innovation of the various stakeholders
- Produce animations or photorealistic renderings for clients, marketing
- Integrate the model in virtual or augmented reality for an almost real rendering
In conclusion, carrying out design studies in 3D is so obvious that it has become commonplace, as the technical and commercial advantages are so many.
But for each company and in a context of exacerbated competition, it is important to add the business component. Dedicated modules or “add-ons” can significantly increase the performance of a 3D tool.
In order to meet the current requirements of electrical design offices and the cabling sector, FTZ has integrated 3D into its products for several years:
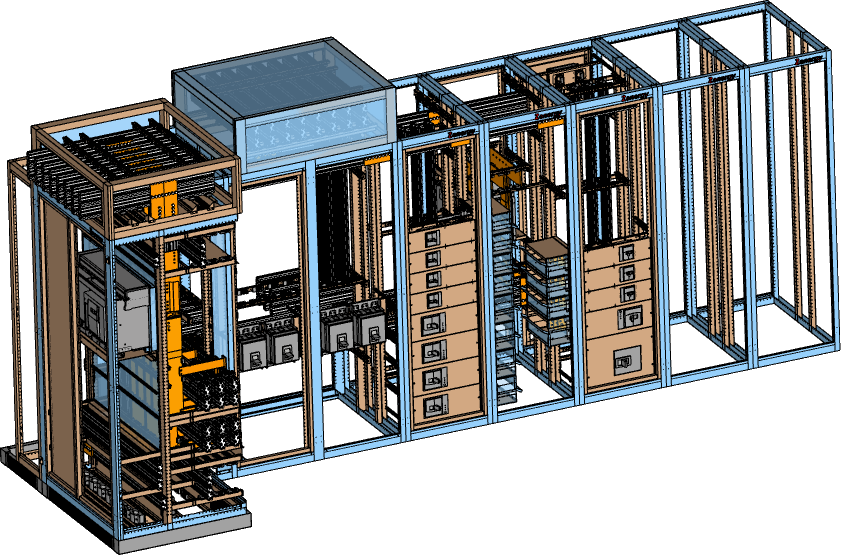
In industrial installations, electrical cabinets and for routing wires and cables with SchemELECT and FTZ-Panel 3D
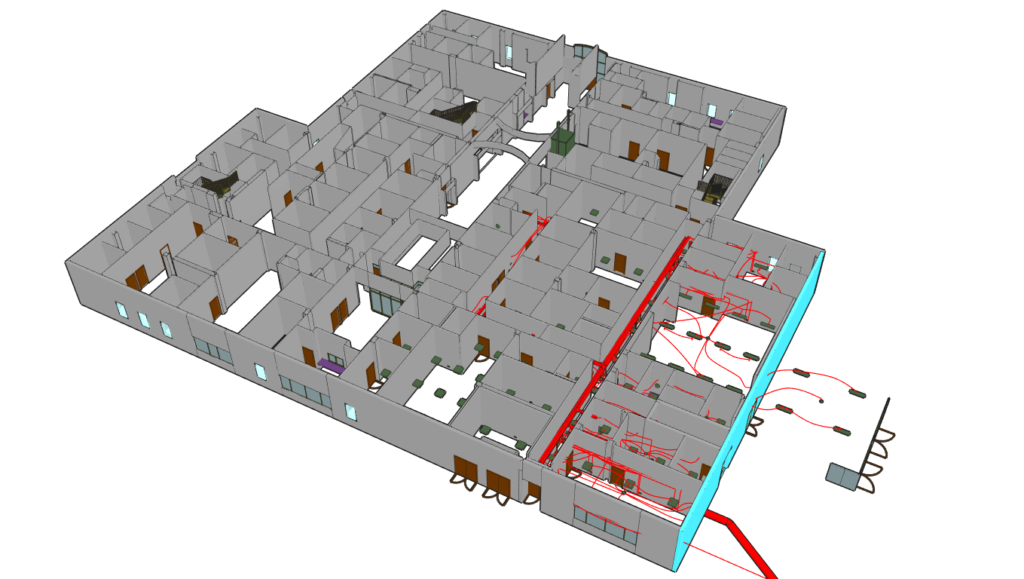
In buildings (in BIM or not) and for cable routing with SchemBAT and FTZ-BIM
